Transfer Learning for Automated Breast Cancer Detection and Segmentation: Development and Evaluation of a Web Application for AI Assisted Mammogram Analysis
Aim and Research Question(s)
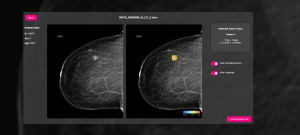
This thesis developed and evaluated "AIRA - AI Radiology Assistant for mammography", an AI tool for automated detection and segmentation of breast tumors in mammograms, focusing on (1) segmentation accuracy compared to expert annotations, and (2) analysis speed versus expert interpretation time.
Background
Breast cancer is the most common cancer worldwide and a leading cause of death among women [1]. In low- and middle-income countries, a shortage of radiologists delays diagnosis, leading to poorer outcomes [2]. Early detection is critical to improve survival rates [3], highlighting the urgent need for faster, automated diagnostic tools to support mammogram analysis.
Methods
The U-Net model with an EfficientNetB0 encoder was implemented using Transfer Learning, with a baseline version (frozen encoder) and a fine-tuned version (last 25 encoder layers unfrozen).
- Dataset: CSAW-CC mammography dataset
- Patch-based training: Patches of 128x128 extracted from healthy and cancerous images
- Evaluation metrics: DSC, IoU, Accuracy, Precision, Recall, AUC
- Usability Testing: SUS evaluation and expert timing comparison
Results and Discussion
Detection Metrics:
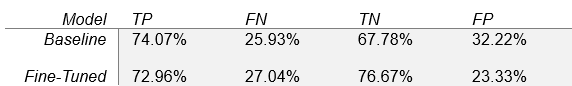
- Fine-tuning improved non-tumor classification from 67.78% to 76.67%, reducing false positives
- Overfitting was observed in both models, highlighting the need for more diverse data
- SUS Score: 95.71 (Excellent usability)
- Processing Time: AI: 9-13 seconds per Image; Radiologist: 4-5 Minutes per Image
Conclusion
The developed AI tool showed promising performance in tumor segmentation and significantly reduced analysis time compared to radiologists. Fine-tuning improved classification balance, and the high SUS score confirmed excellent usability. Further work is needed to address overfitting and test the model on more diverse data.
References
[1] WHO. (2024). Breast cancer. WHO World Health Organization. [2] Anderson et al. (2021). The Global Breast CancerInitiative: A strategic collaboration to strengthen health care for non communicable diseases. The Lancet. Oncology, 22(5), 578–581. [3] American Cancer Society. (2024). Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2024-2025.