Interactive video-based E-Learning for Digital Health Literacy: Conception, Development and UX Evaluation of a Prototype to Support the Digital Health Literacy of Registered Nurses
Aim and Research Question(s)
The primary objective of this study was the conception, development and user experience (UX) evaluation of an interactive video-based e-Learning prototype to support the digital health literacy of registered nurses. To achieve this goal, the following research questions (RQ) were derived:
- Which digital health literacy content could empower registered nurses in their patient education process and what are the requirements for an interactive E-learning video to provide such content? (RQ 1)
- Does the developed interactive E-learning video meet the experience expectations of registered nurses? (RQ 2)
Background
The Austrian Health Promotion Strategy aims to enhance the health literacy of its citizens to achieve longer lives in good health. However, Austria’s low health literacy ranking among EU countries poses a significant challenge. [1, 2] Simultaneously, the rapid digitalisation in the healthcare sector presents opportunities, but both patients and healthcare professionals face difficulties in adapting to this evolving landscape [3]. Registered nurses are in a key position to have a positive impact for this problem, as they can offer guidance during patient education [4].
Methods
The study adopted a one-group posttest research design. To identify relevant content and requirements, a literature review was conducted. Based on this results, the prototype was developed using the ADDIE model, comprising the five steps Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation and Evaluation. A modular, animated video was produced, featuring interactive elements such as quizzes. The UX of the prototype was assessed by 21 registered nurses through the standardized User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ) [5].
Results and Discussion
The developed interactive e-Learning video provides information about searching for health information online, evaluating the reliability of online sources, ensuring online safety and security and offers an overview of reliable websites and useful checklists. The results demonstrate a positive evaluation across all six dimensions of the UEQ (scale from -3 to 3, positive rating >0.8), including Attractiveness (mean=2.24), Perspicuity (mean=2.64), Efficiency (mean=1.88), Dependability (mean=1.75), Stimulation (mean=1.9) and Novelty (mean=1.64). Comparative benchmarking positioned the prototype in the top 10% among other products.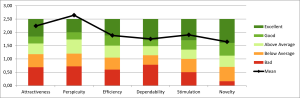 Figure 1: UEQ Results - Benchmark Mean
Figure 1: UEQ Results - Benchmark Mean
Conclusion
This study highlights the potential of e-Learning tools to enhance health literacy, contributing to improved healthcare. Future research should measure changes in digital health literacy levels, refine content and requirements, assess interactive element effectiveness and consider technical aspects and accessibility. Bridging the gap between low health literacy and underutilised digital tools can contribute to a more efficient and patient-centered healthcare system, aligning with the health promotion objectives in Austria.
References
[1] BMG. (2016). [2] ÖPGK. (2021). [3] Greenhalgh et al. (2018). [4] Navarro Martínez et al. (2021) [5] Schrepp, D. M. (2019).
