Usability evaluation of LLM-supported Alexa Skills for the voice-controlled scheduling of robot vacuum cleaners and for personal emergency response systems for fall prevention and support in everyday life for elderly people, a pilot study
Aim and Research Question(s)
This thesis explores the use of LLMs for VUIs in PERS, to examine if they improve usability. Furthermore, it examines the usability of LLMs in VUIs for vacuum appointment scheduling in PERS. This thesis strives to answer the following research questions: How does the use of an LLM affect the usability in conversations of the SC2 scenarios? How does the use of an LLM affect the usability of a vacuum scheduling voice skill of a smart robotic vacuum cleaner?
Background
The increasing life expectancy in Austria stired more interest in maintain elderly people's independence in every day life in order to conserve resources in the healthcare sector [1][2]. PERS use amongst other technologies VUIs to support the elderly and respond immediatly, however unexpected voice input and non-linear user answers cause errors and limit the capabilities of these voice models [3].
Methods
A quantitative usability pilot study approach using non-probability sampling is chosen. Ten test subjects, are recruited using a purposive snowball sampling approach in order to test two skill pairs. All four VUIs are assessed using System Usability- and Voice Usability Scale, to compare them with each other.
Results and Discussion
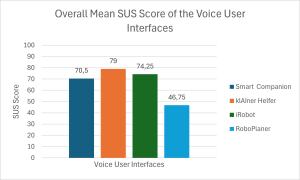
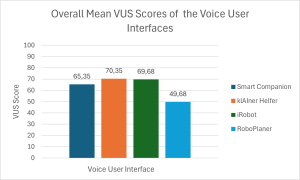
The mean total SUS score for the klAIner Helfer is 79, it therefore outperformed the smart companion skill, which received a mean total SUS score of 70,5 and showed that the usage of LLM integrations can benefit the user. The iRobot achieved a far higher total mean SUS score than the RoboPlaner. the klAIner Helfer skill performed similarly to the SUS results. With a total mean VUS score of 70,35 it outperformed the smart companion VUI. The RoboPlaner mean VUS score of 49,68 is much lower than for the iRobot’s 69,68.
Conclusion
The klAIner Helfer VUI for comparison with the Smart Companion achieved higher SUS and VUS scores, which implies a beneficial impact of LLM usage for the tested Smart Companion use case. The results of the vacuum scheduling skill’s pair indicates that due to the low scores of the self-developed VUI it needs redesign and complexity reduction. It has to be said that due to the limitations of this study, further research is advised to validate the highlighted potential of this study's results.
References
[1] Y.-R. R. Chen and P. J. Schulz, ‘The Effect of Information Communication Technology Interventions on Reducing Social Isolation in the Elderly: A Systematic Review’, J Med Internet Res, vol. 18, no. 1, p. e18, Jan. 2016, doi: 10.2196/jmir.4596.; [2] M. Holzer, ‘Österreichische Gesundheitsbefragung 2019’, 2019.; [3] Harvill et al., ‘Significant ASR Error Detection for Conversational Voice Assistants’, in ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Korea, Republic of: IEEE, Apr. 2024, pp. 11606–11610. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10448230.
